The Evolution of Electromagnetic Induction Testing
February 12, 2026
Non-destructive testing methods have evolved significantly to meet the demands of modern infrastructure and manufacturing. Among these techniques, electromagnetic induction testing has become a critical tool for identifying flaws without damaging materials. Understanding the evolution of electromagnetic induction testing highlights how this technology has advanced to improve accuracy, efficiency, and reliability across industries.
What Is Electromagnetic Induction Testing
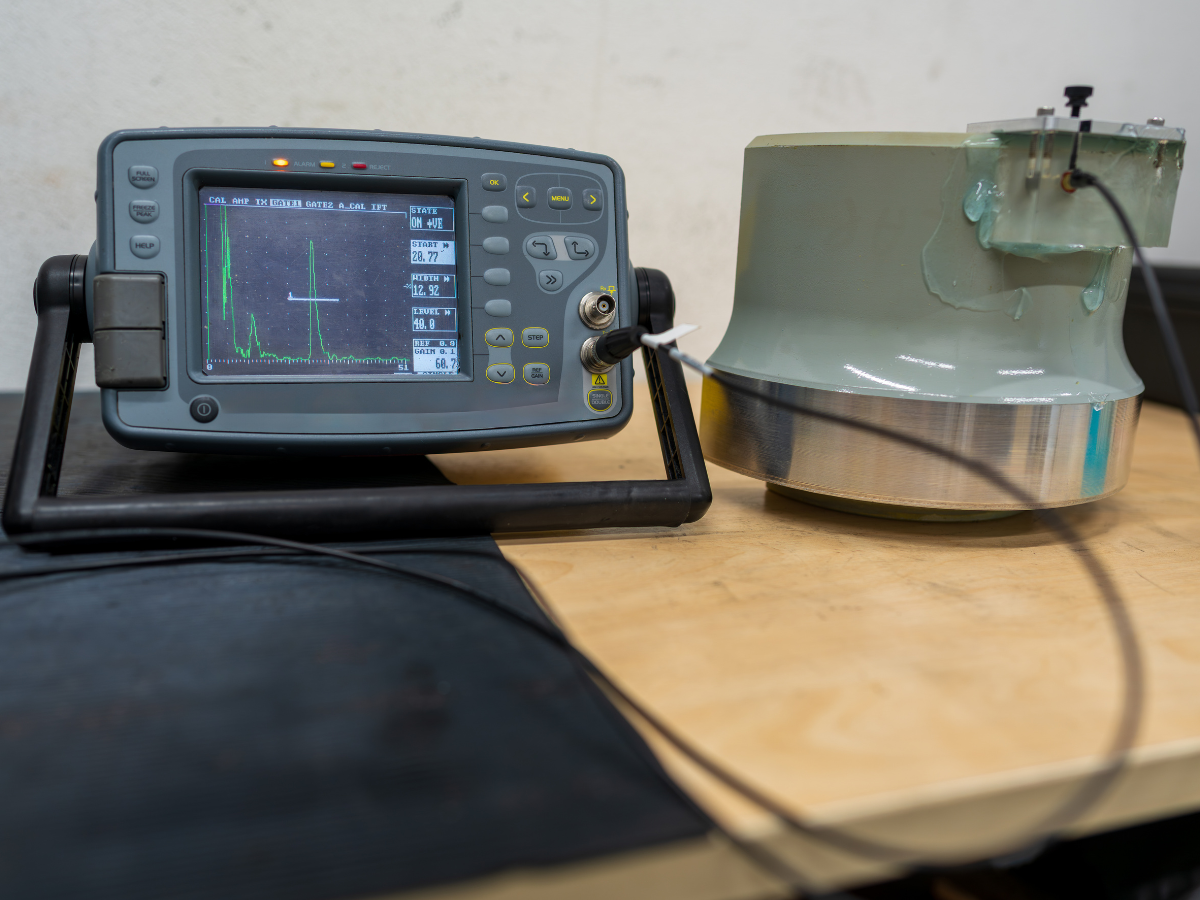
Electromagnetic induction testing is a non-destructive testing method that uses electromagnetic fields to detect surface and near-surface flaws in conductive materials. It is most commonly associated with eddy current testing, where alternating current creates magnetic fields that interact with the material being inspected.
Changes in these fields indicate defects such as cracks, corrosion, or material inconsistencies.
Early Foundations of Electromagnetic Testing
The origins of electromagnetic testing date back to early discoveries in electromagnetism during the nineteenth century. Scientists identified that electrical currents could induce magnetic fields and that conductive materials responded predictably to these forces.
These early principles laid the groundwork for practical eddy current inspection methods used in industrial applications.
Adoption in Industrial Inspection
By the mid twentieth century, electromagnetic induction testing gained traction in industries such as aerospace, power generation, and manufacturing. Early inspection systems were primarily analog and required skilled interpretation.
Despite limitations, these methods offered faster inspection times and reduced downtime compared to destructive testing techniques.
Advancements in Equipment and Signal Processing
Technological improvements dramatically changed electromagnetic induction testing capabilities. Digital signal processing allowed inspectors to detect smaller defects with greater precision.
Modern equipment now features:
- enhanced sensitivity
- improved depth penetration
- real-time data visualization
- portable inspection tools
These advancements expanded the range of applications and improved reliability.
Integration With Modern NDT Techniques
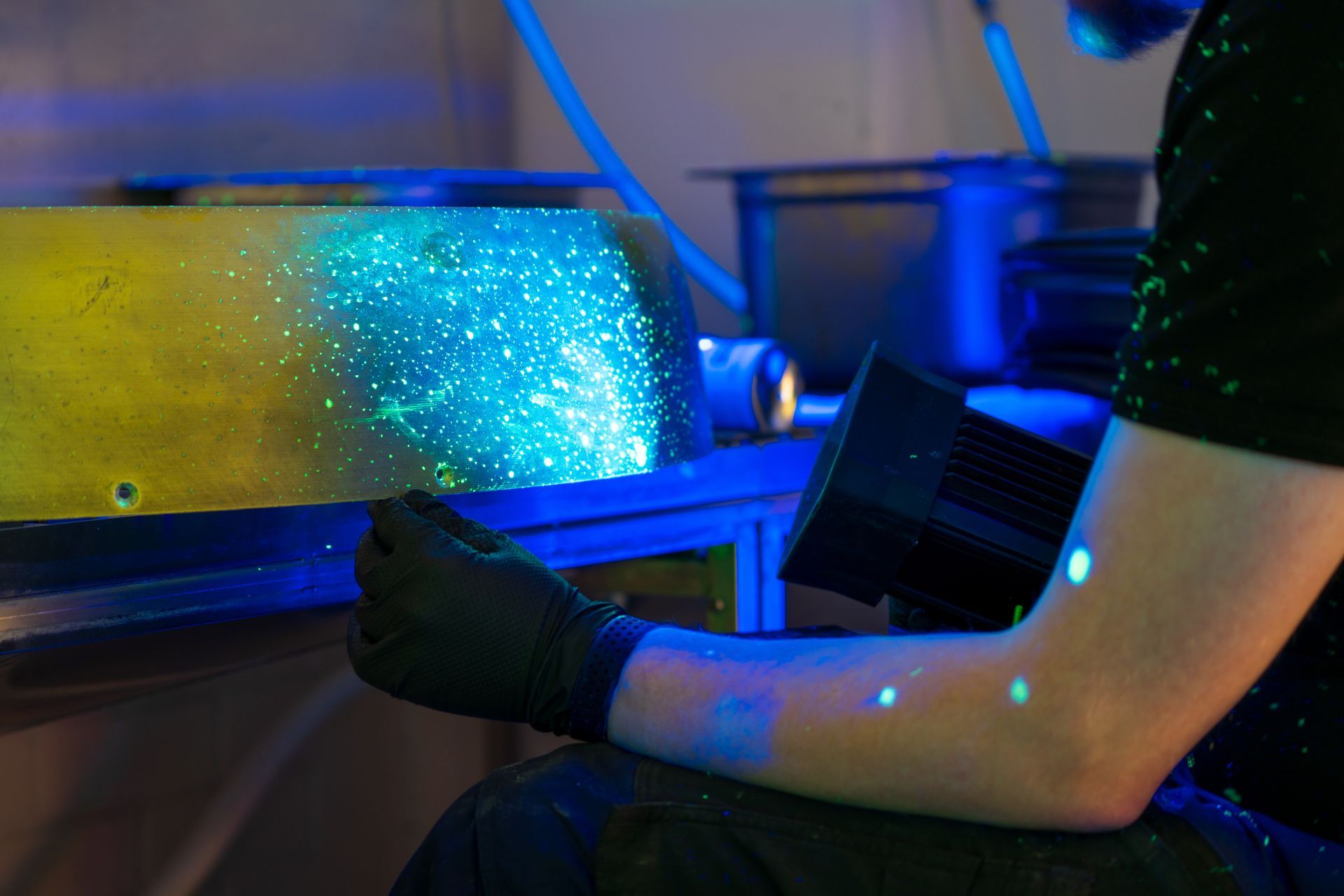
Today, electromagnetic induction testing is often used alongside other non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle testing. This multi-method approach provides a more comprehensive assessment of material integrity.
Combining inspection techniques helps ensure accurate evaluation of complex structures.
Applications Across Industries
Modern eddy current testing plays a vital role in:
- pipeline inspection
- aerospace component evaluation
- heat exchanger tube testing
- structural weld assessment
- corrosion detection
Its ability to detect flaws quickly without surface preparation makes it highly efficient for routine inspections.
The Role of Automation and Data Analysis
Recent advancements include automated scanning systems and advanced data analysis software. These tools reduce human error and increase consistency.
Automation supports higher inspection volumes while maintaining accuracy, which is essential for large scale infrastructure and manufacturing environments.
Why Electromagnetic Induction Testing Continues to Evolve
As materials, manufacturing methods, and safety standards advance, inspection technologies must keep pace. The continued evolution of electromagnetic induction testing reflects the growing demand for precise, non-invasive inspection solutions.
Ongoing research focuses on improving resolution, expanding material compatibility, and integrating AI-assisted analysis.
Advancing Inspection Through Innovation
The evolution of electromagnetic induction testing demonstrates how scientific principles can transform into indispensable industrial tools. From early electromagnetic discoveries to modern digital inspection systems, this method continues to enhance safety and reliability across industries. Steel City NDT delivers advanced electromagnetic induction and eddy current testing services to support accurate inspections, regulatory compliance, and long-term asset integrity.





